This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my links.
Understanding Maine Coon Cat Lifestyle Health Issues
Maine Coon cats carry a unique set of health challenges influenced significantly by their lifestyle. While genetic health issues are an important aspect of their overall health, in this article, we’ll focus on Maine Coon Cat Lifestyle Health Issues, which are often more controllable and preventable.
By understanding and managing these lifestyle factors, owners can play a crucial role in mitigating risks and ensuring their furry companions lead a healthier and more vibrant life.
Maine Coon Most Common Lifestyle Health Issues
1. Obesity in Maine Coon Cats
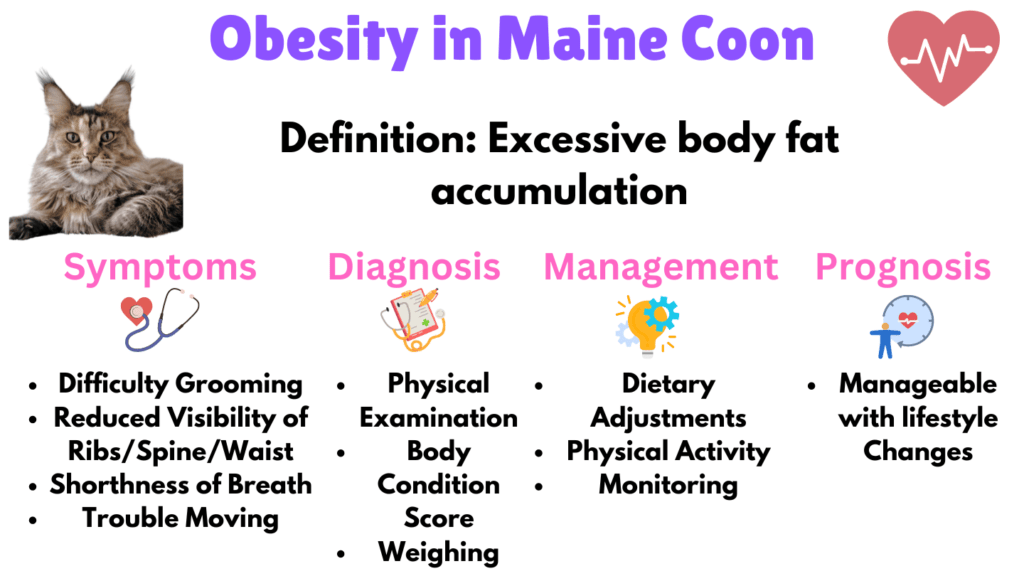
Obesity is a prevalent concern among Maine Coons, primarily due to their large stature and sedentary tendencies. This condition impacts not just their mobility and quality of life but also increases their risk for a slew of secondary health issues, such as diabetes mellitus, joint pain, and cardiovascular problems.
Symptoms
Maine Coon owners should look out for several indicators of obesity:
- Difficulty Grooming: Struggling to groom or reach certain areas of their body.
- Reduced Visibility of Ribs, Spine, and Waistline: The ribs, spine, and waistline become less visible or palpable due to excess weight.
- Lethargy: Exhibiting lethargy or a decreased interest in play, which is unusual for this typically active breed.
- Shortness of Breath: Experiencing shortness of breath or panting after minimal physical exertion.
- Excess Fat Deposits: Noticing fat deposits over the lower back, face, and limbs.
- Trouble Moving: Difficulty jumping or moving around, which can lead to decreased mobility and reluctance to exercise.
Diagnosis
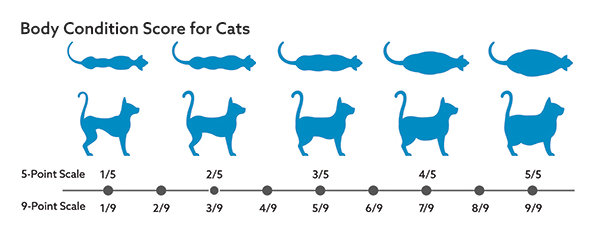
Veterinarians diagnose obesity in Maine Coons using a combination of methods. A thorough physical examination helps establish the cat’s body condition score by evaluating fat deposits over key areas such as the ribs, spine, and tail base. Weighing the cat and comparing its weight to breed-specific ideal weight ranges is crucial. Our Maine Coon weight calculator can assist in determining the ideal estimated weight.
Management
Managing obesity in Maine Coon cats involves a multifaceted approach. A controlled feeding plan, possibly incorporating a specially formulated weight management diet, is essential.
Regular, moderate exercise can help burn calories and maintain muscle mass; this might include interactive play sessions or the use of cat exercise wheels that accommodate larger breeds. Continuous monitoring by a veterinarian is also crucial, with regular follow-ups to monitor the cat’s weight and make necessary adjustments to their diet or exercise plan.
Implications of Obesity in Maine Coon Cats
Obesity in Maine Coon cats can lead to a host of secondary health conditions that can significantly diminish their quality of life and life expectancy.
Excessive weight can strain the heart, potentially leading to heart disease and increased blood pressure. It also places additional burden on the joints, which can exacerbate or lead to the development of arthritis, particularly in a breed already prone to joint issues due to their large size.
Furthermore, obesity can impair respiratory function, making it difficult for the cat to breathe even during light activity. Over time, these complications can lead to a decreased ability to enjoy daily activities, reduced overall health, and a shortened lifespan.
2. Diabetes in Maine Coon Cats
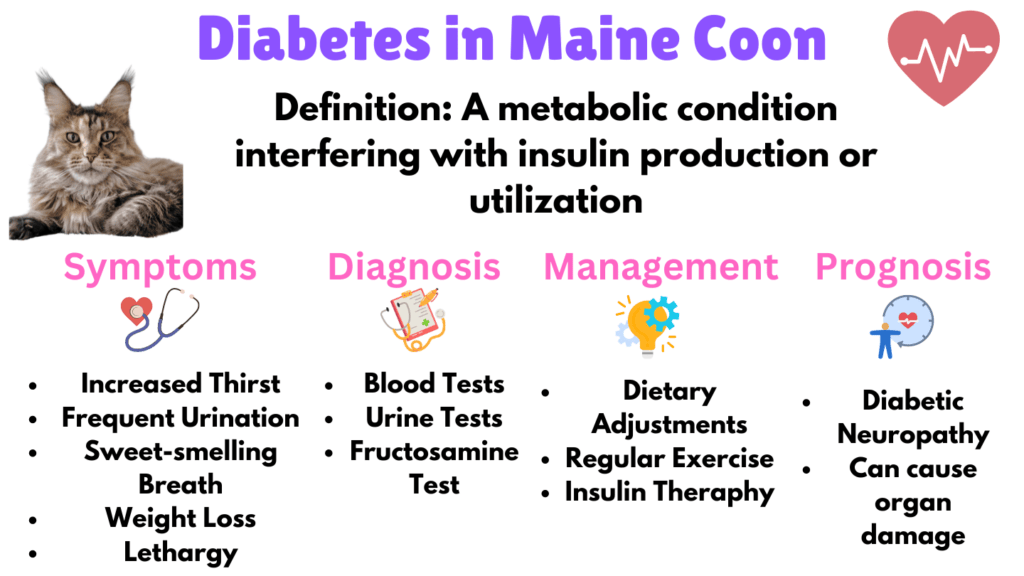
Diabetes Mellitus is a significant health issue for Maine Coon cats, particularly those that are overweight or obese as discussed earlier. This metabolic condition interferes with the cat’s ability to produce or properly use insulin, which is crucial for regulating blood sugar levels
Symptoms
Maine Coons with diabetes exhibit a variety of signs that owners should watch for:
- Increased Thirst: Drinking more water than usual.
- Frequent Urination: Increased frequency and volume of urination.
- Increased Appetite: A noticeable increase in hunger.
- Weight Loss: Despite having an increased appetite, affected cats may lose weight.
- Lethargy: Reduced energy levels and less enthusiasm for activities they previously enjoyed.
- Weakness in the Hind Legs: Diabetic neuropathy can cause weakness or an abnormal gait.
- Poor Coat Condition: The coat may become dull or unkempt.
- Vomiting: Occasional vomiting due to elevated blood sugar levels.
- Sweet-Smelling Breath: A sweet, fruity odor to the breath, which is a sign of ketosis in severe cases.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing diabetes in Maine Coon cats involves several important tests. First, blood tests measure the cat’s blood glucose levels, which tend to be elevated in diabetic cats. Urine tests are also conducted to detect the presence of glucose and ketones, both indicative of diabetes.
Additionally, the fructosamine test provides an average blood glucose level over the past two to three weeks, offering a comprehensive view of the cat’s glucose management.
Management
Managing diabetes in Maine Coon cats requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary adjustments, exercise, and possibly insulin therapy.
Dietary management is crucial, involving a low-carbohydrate, high-protein diet to help regulate blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity not only helps to reduce blood glucose levels but also maintains a healthy weight, which is especially important for diabetic cats.
Some cats may require insulin injections to manage their condition, which owners can administer at home after receiving proper training from their veterinarian. Regular monitoring of blood sugar levels, either at home or through periodic veterinary check-ups, is essential to ensure the treatment plan is effective and the cat’s diabetes is well controlled.
Implications of Diabetes in Maine Coon Cats
Diabetes, if not properly managed, can have severe consequences for Maine Coon cats. Chronic high blood glucose levels can lead to damage in various organs, including the eyes, kidneys, and heart. One of the more immediate risks of unmanaged diabetes is diabetic neuropathy, which manifests as weakness in the legs and can severely affect mobility.
Additionally, diabetic cats are at a higher risk of developing urinary tract infections, which can further complicate their overall health status.
3. Dental Problems in Maine Coon Cats
Dental problems are a common concern for Maine Coon cats, affecting their overall health and well-being. These issues include periodontal disease, tooth decay, and gingivitis, all of which can lead to significant discomfort and more serious health complications if left untreated.
Symptoms
Maine Coon owners should look out for several indicators of dental problems:
- Bad breath, which is often one of the first signs of dental disease.
- Visible tartar or plaque buildup on the teeth.
- Red, swollen, or bleeding gums, indicating inflammation or infection.
- Difficulty eating or a preference for softer foods, which may suggest pain or discomfort in the mouth.
- Pawing at the mouth or drooling, which can also indicate dental discomfort.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing dental problems in Maine Coon cats typically involves a thorough examination by a veterinarian. This examination includes a visual inspection of the mouth for signs of dental disease, such as inflamed gums, tartar, and missing or loose teeth.
X-rays may also be required to assess the health of the jaw and the roots of the teeth beneath the gum line, which are not visible during a routine examination.
Management
Effective management of dental problems in Maine Coon cats includes both preventive and reactive measures. Regular professional cleanings by a veterinarian are essential to remove plaque and tartar buildup.
Daily brushing with cat-specific toothpaste helps prevent the accumulation of plaque. Specialized diets or dental chews can also aid in reducing plaque through mechanical action.
In cases of severe dental issues such as stomatitis—a painful condition characterized by severe inflammation of the mouth—more intensive treatments like tooth extractions and long-term medication may be necessary.
Implications
If left untreated, dental problems can lead to more severe health issues in Maine Coon cats. Bacteria from the mouth can enter the bloodstream, potentially damaging vital organs such as the kidneys, heart, and liver.
Chronic dental disease can also lead to poor general health, weight loss, and a significantly reduced quality of life due to ongoing pain and discomfort.
4. Heart Disease in Maine Coon Cats
Heart disease is a significant concern for Maine Coon cats, with both genetic and lifestyle factors playing crucial roles. While some heart conditions, such as hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), are hereditary, lifestyle factors like diet and exercise are equally important in maintaining heart health.
Poor lifestyle choices, such as a high-fat diet and lack of physical activity, can exacerbate these conditions, leading to heart failure or arrhythmias.
Symptoms
Maine Coon owners should be aware of several signs that may indicate heart disease:
- Lethargy: A noticeable decrease in energy levels or reluctance to engage in physical activities.
- Difficulty breathing: Rapid or labored breathing, even when the cat is at rest.
- Coughing: Persistent coughing or wheezing, especially after exercise.
- Loss of appetite: A sudden decrease in interest in food, leading to weight loss.
- Fainting or collapse: Episodes of fainting or sudden collapse, often triggered by exertion.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing heart disease in Maine Coon may include a physical examination where the vet listens to the heart and lungs for abnormalities such as murmurs or irregular heartbeats.
An echocardiogram, which is an ultrasound of the heart, may be conducted to visualize its structure and function, identifying conditions like hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) that are common in Maine Coons. An electrocardiogram (ECG) might also be used to measure the electrical activity of the heart and detect arrhythmias, while blood tests can check for biomarkers indicative of heart disease.
Management
Effective management of heart disease in Maine Coon cats involves a combination of lifestyle adjustments and medical treatments. A diet low in fats and rich in nutrients that support heart health is crucial.
Encouraging regular, moderate physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and improves cardiovascular fitness, though it’s important to avoid overexertion and monitor your cat’s response to exercise.
Medication may be prescribed to manage symptoms and improve heart function, including beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, or diuretics, depending on the specific condition.
Implications
Potential complications include congestive heart failure, a condition where the heart cannot pump blood effectively, leading to fluid buildup in the lungs and other organs.
Thromboembolism, the formation of blood clots that can obstruct blood flow to vital organs, is another serious risk, causing pain and potentially life-threatening conditions.
Chronic pain, difficulty breathing, and fatigue from untreated heart disease can significantly impact your cat’s well-being and longevity.
5. Stress and Anxiety in Maine Coon Cats
Maine Coons are known for their social and affectionate nature, making them particularly susceptible to stress and anxiety if they don’t receive enough attention or stimulation. These cats thrive on interaction and companionship, and a lack of these can lead to behavioral and health issues.
Symptoms
Maine Coon owners should look out for several indicators of stress and anxiety:
- Excessive grooming or self-mutilation, often resulting in bald spots.
- Changes in appetite, such as eating too much or too little.
- Increased vocalization, including yowling or meowing more than usual.
- Hiding or avoiding interaction, which is out of character for these sociable cats.
- Aggression towards people or other pets, displaying unusual irritability.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing stress and anxiety in Maine Coon cats involves observing their behavior and noting any changes. A veterinarian can help rule out medical conditions that might cause similar symptoms. They may suggest a behavioral assessment to identify specific stressors in the cat’s environment.
Management
Managing stress and anxiety in Maine Coon cats focuses on increasing their sense of security and providing ample stimulation. Interactive play is essential; toys that mimic prey and games that involve chasing or pouncing can be very effective.
Ensuring your Maine Coon has plenty of opportunities for social interaction, whether with humans or other pets, is also important. In some cases, pheromone diffusers or calming supplements might be recommended by your veterinarian to help soothe your cat’s nerves.
Implications
If left unaddressed, stress and anxiety can lead to more serious health and behavioral problems in Maine Coon cats. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, making cats more susceptible to illnesses. Behavioral issues such as aggression or inappropriate elimination can also strain the bond between pet and owner.
6. Gastrointestinal Issues in Maine Coon Cats
Overfeeding or feeding Maine Coons an improper diet can lead to gastrointestinal problems such as constipation or diarrhea. Proper diet management is crucial for maintaining their digestive health and overall well-being.
Symptoms
Maine Coon owners should be aware of several signs that may indicate gastrointestinal issues:
- Vomiting or regurgitating food frequently.
- Changes in stool consistency, ranging from diarrhea to constipation.
- Abdominal pain or discomfort, which might be indicated by vocalizations or restlessness.
- Loss of appetite or overeating, leading to weight loss or obesity.
- Lethargy and decreased activity levels.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing gastrointestinal issues in Maine Coon cats often requires a multifaceted approach. A veterinarian will conduct a physical examination and review the cat’s dietary history.
Blood tests, fecal exams, and imaging studies like X-rays or ultrasounds may be necessary to identify underlying issues such as blockages, infections, or organ dysfunction.
Management
Managing gastrointestinal issues in Maine Coon cats involves dietary adjustments and ensuring proper hydration. Feeding a balanced diet that is appropriate for their age, weight, and activity level is key.
High-fiber foods can help regulate digestion and prevent constipation, while avoiding fatty or rich foods can reduce the risk of diarrhea. Providing fresh water at all times encourages adequate hydration, which is vital for digestive health.
In some cases, veterinarians may recommend probiotics or digestive enzymes to support gut health. Regular feeding schedules and portion control can also help maintain a healthy digestive system.
Implications
Chronic diarrhea or constipation can cause dehydration, malnutrition, and weight loss. Prolonged digestive discomfort can also impact a cat’s quality of life, leading to reduced activity and increased stress.
7. Skin Problems in Maine Coon Cats
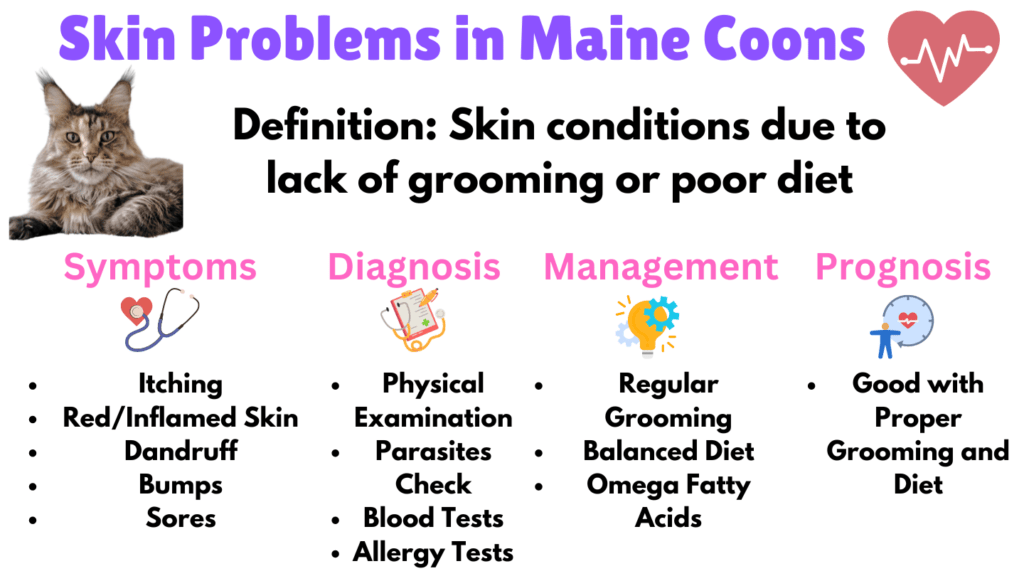
Maine Coon cats are known for their luxurious coats, but maintaining their skin and fur health requires diligent care. Lack of grooming or an inadequate diet can result in various skin conditions, including allergies, dermatitis, and infections.
Symptoms
Maine Coon owners should look out for several indicators of skin problems:
- Itching and scratching, which can lead to hair loss and skin damage.
- Red, inflamed, or scaly skin, indicating irritation or infection.
- Excessive dandruff or dry, flaky skin.
- Presence of bumps, sores, or scabs on the skin.
- Changes in coat quality, such as dullness or thinning fur.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing skin problems in Maine Coon cats includes checking for external parasites like fleas or mites, as well as conducting skin scrapings and allergy tests to identify potential irritants or allergens. Blood tests may also be performed to rule out underlying systemic issues.
Management
Managing skin problems in Maine Coon cats involves a combination of grooming and dietary interventions. Regular grooming helps remove loose hair, dirt, and potential allergens from the coat, reducing the risk of skin irritation.
Using appropriate grooming tools, such as brushes designed for long-haired cats, can make this process more effective. Ensuring a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, including omega fatty acids, supports skin health and coat quality. In some cases, supplements may be recommended to address specific deficiencies.
Implications
Chronic skin irritation can result in secondary infections, causing pain and discomfort. Persistent scratching and grooming can lead to hair loss and skin damage, impacting the cat’s appearance and overall health.
Quick Tips for Keeping Your Maine Coon Healthy
To help your Maine Coon thrive, remember these essential tips:
- Regular Vet Visits: Schedule annual check-ups to catch any health issues early.
- Balanced Diet: Ensure your cat’s diet is tailored to their specific needs, with a focus on heart health, digestive health, and skin health.
- Exercise and Play: Keep your Maine Coon active with interactive toys and regular playtime to prevent obesity and manage stress.
- Grooming Routine: Establish a consistent grooming schedule and routine to maintain their coat and skin health. Also consider other grooming requirements such as dental care, nail trimming, and ear cleaning.
- Monitor Behavior: Pay attention to any changes in behavior or physical condition, and consult your vet if you notice anything unusual.
- Love and Attention: Spend quality time with your Maine Coon to keep them emotionally satisfied and reduce anxiety.
- Hydration: Ensure your cat has access to fresh water at all times to support overall health.
Final Thoughts on Maine Coon Cat Lifestyle Health Issues
Maintaining the health of your Maine Coon cat involves a combination of proper diet, regular exercise, and attentive care. Many of the lifestyle health issues discussed can be prevented or at least mitigated through proactive measures. As a Maine Coon lover, it’s up to you to take action to ensure your cat’s well-being.
By staying informed about potential health issues and implementing these practical tips, you can help your feline friend enjoy a long and vibrant life. A little extra care goes a long way in preventing and managing the lifestyle health issues that Maine Coons are prone to.
Meet Sean, a fintech whiz with a penchant for pet purrs and blockchain buzz. After a decade of fintech feats, Sean’s tech talents leaped from ledger lines to litter lines, driven by a passion for pets and a vision for a more connected pet care community. With three critter companions as co-pilots, Sean launched this blog to share a treasury of pet-friendly tech tips and tales.



