This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking on my links.
Getting Started: Maine Coon Cat Health Issues
Maine Coon cats, face unique health challenges that every owner should be aware of. This comprehensive post about all the health issues of Maine Coon cats will cover both genetic and lifestyle-related problems.
Understanding these issues is crucial for maintaining the well-being of these gentle giants. We’ll start by discussing genetic health issues, which are harder to control, and then move on to lifestyle health issues, which are often influenced by the owner’s care and attention.
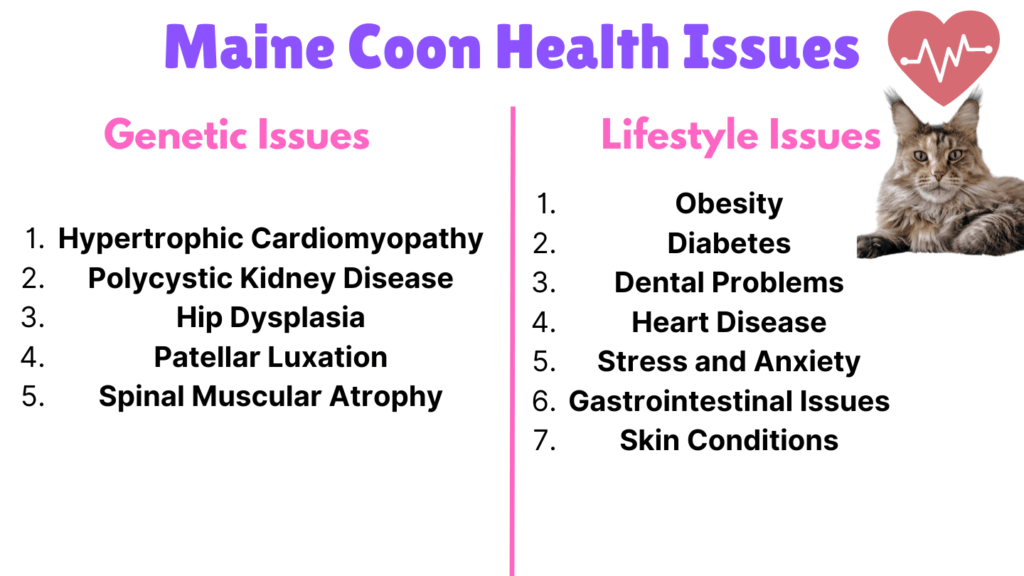
Genetic Health Issues of Maine Coons
Genetic health issues can significantly impact the well-being of Maine Coon cats, these genetic problems, ranging from heart diseases to joint disorders, often require early detection and proactive management to ensure your furry friend lives a long and healthy life.
Genetic testing plays a vital role in identifying these issues early, allowing for timely interventions and better overall care.
For a thorough guide on the symptoms, diagnosis, and management of genetic issues, read this post >>

1. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
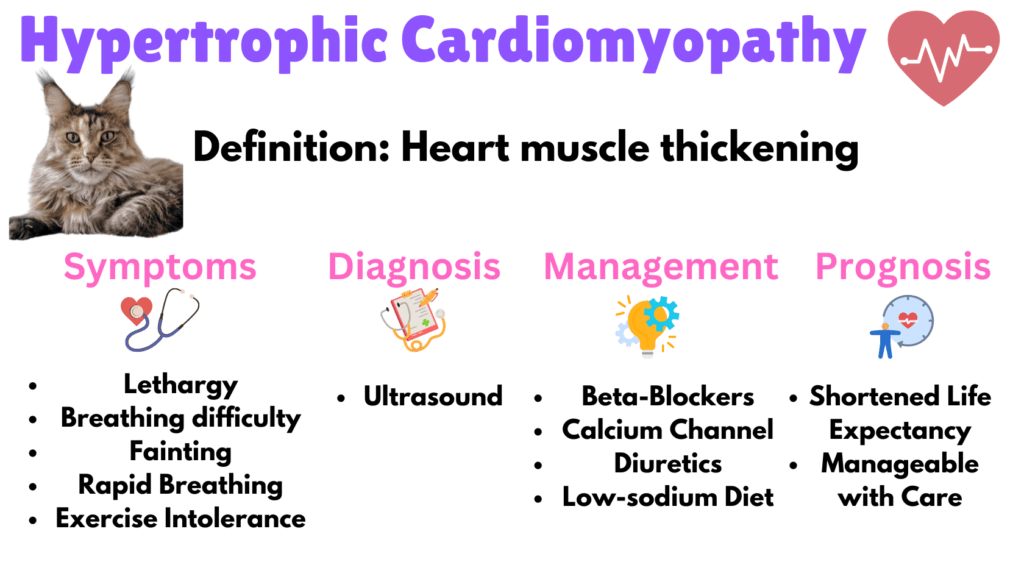
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most common heart disease in Maine Coons, characterized by the thickening of the heart muscle, which impedes its ability to pump blood efficiently.
Symptoms include lethargy, difficulty breathing, and fainting spells. HCM impacts the cat by reducing their activity level and overall quality of life. Early detection and proper management can significantly improve their prognosis.
2. Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) and Kidney Cysts
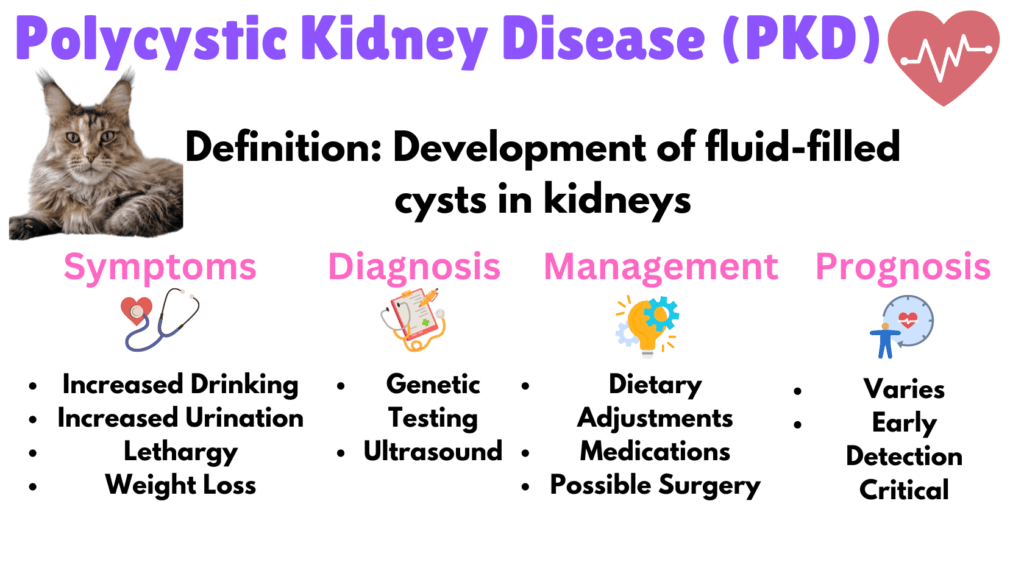
Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) is a genetic disorder marked by the development of fluid-filled cysts in the kidneys, which can lead to renal failure over time. Key symptoms include increased drinking and urination, lethargy, and weight loss. PKD impacts the cat by progressively reducing kidney function, leading to serious health issues.
3. Hip Dysplasia
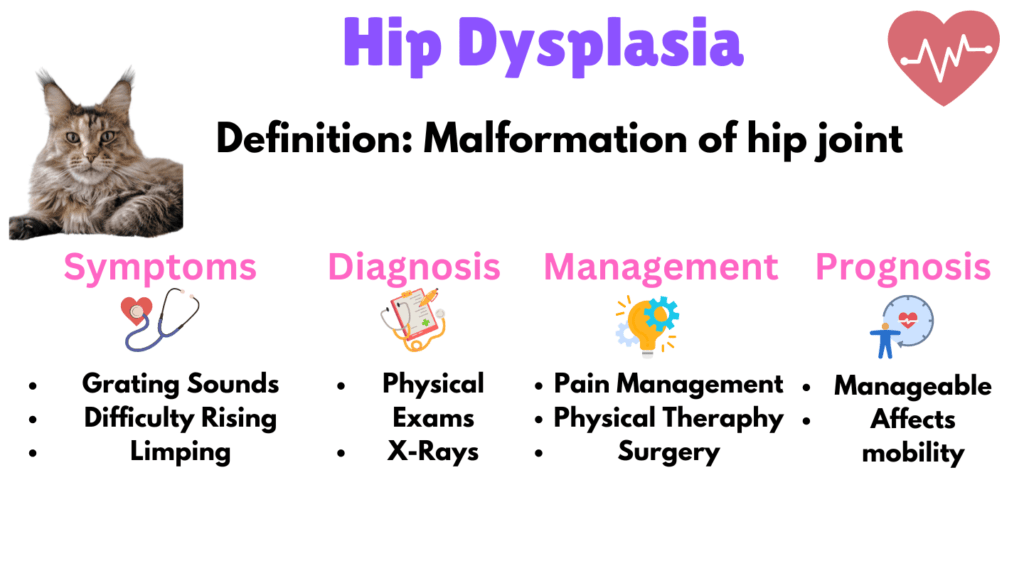
Hip Dysplasia is a structural malformation of the hip joint where the ball of the femur does not fit properly into the hip socket, leading to arthritis and significant mobility issues over time. Symptoms include grating sounds during movement, reduced thigh muscle mass, difficulty rising, and limping. Hip Dysplasia impacts the cat by causing pain and limiting their mobility.
4. Patellar Luxation
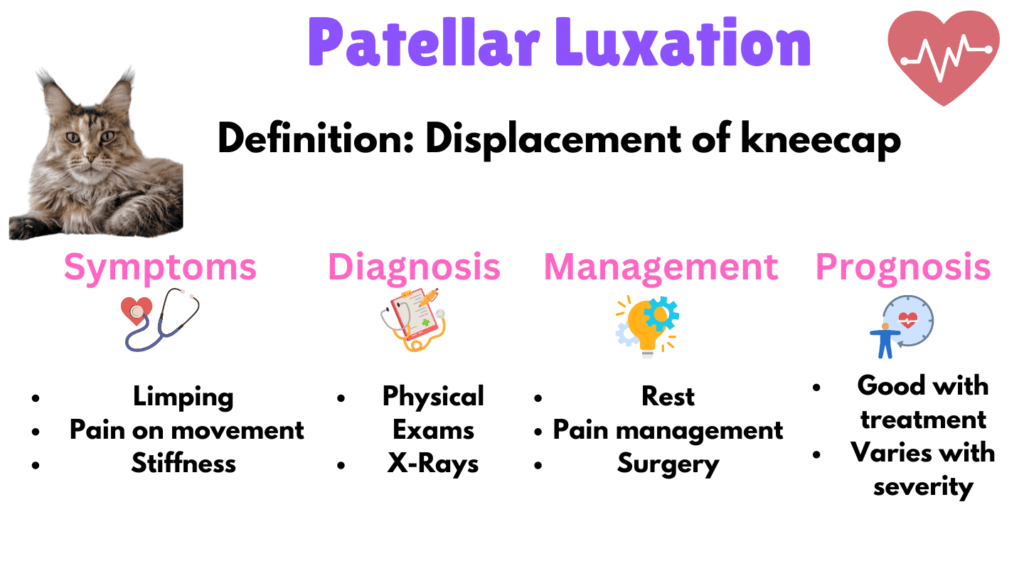
Patellar Luxation occurs when the kneecap slips out of its normal position, leading to pain and mobility issues. Symptoms include hind leg weakness, limping, and pain during activity.
The prognosis varies based on the severity of the condition; some cats lead comfortable lives with mild cases, while more severe cases require ongoing management.
5. Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
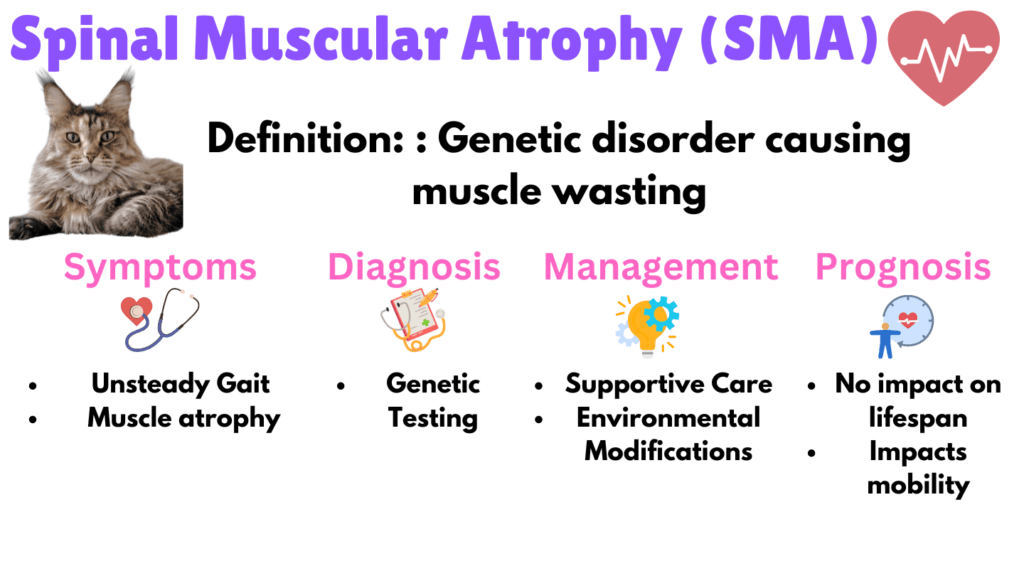
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a genetic disorder caused by the degeneration of spinal cord neurons, leading to progressive muscle wasting and weakness. Symptoms include an unsteady gait, muscle atrophy, and decreased ability to jump. While SMA is non-fatal, it significantly impacts the cat’s mobility and activity levels.
Lifestyle Health Issues of Maine Coons
Lifestyle health issues often stem from factors such as diet, activity level, and environmental stress. Preventive care and maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential to managing these issues and ensuring your Maine Coon leads a happy, healthy life.
6. Obesity
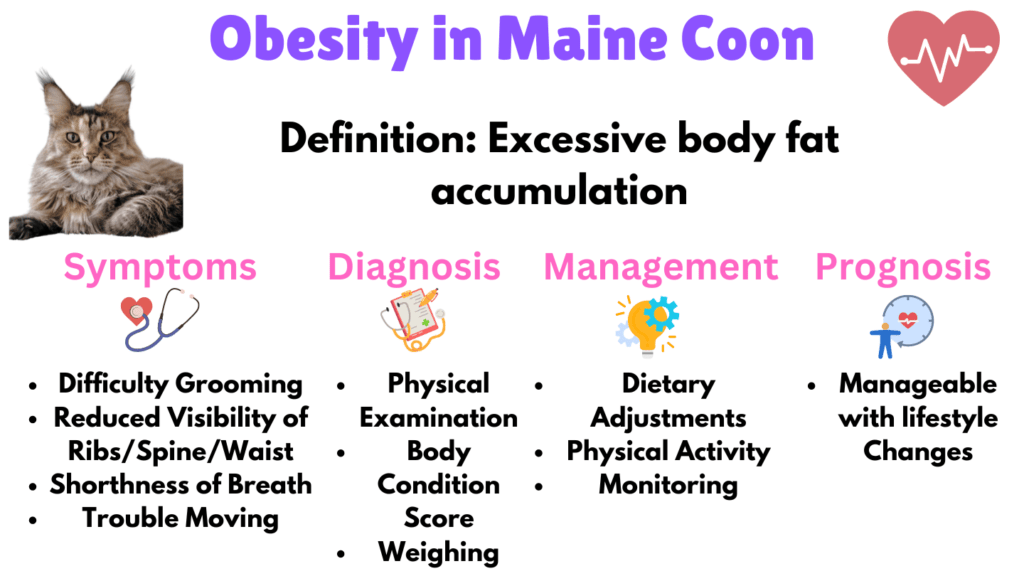
Obesity in Maine Coons is defined as being 20% over their ideal body weight. Due to their large size and sedentary tendencies, this is a common issue.
Symptoms include difficulty grooming, reduced visibility of ribs and spine, lethargy, and shortness of breath. Obesity impacts the cat by increasing the risk of diabetes, joint pain, and cardiovascular problems.
7. Diabetes
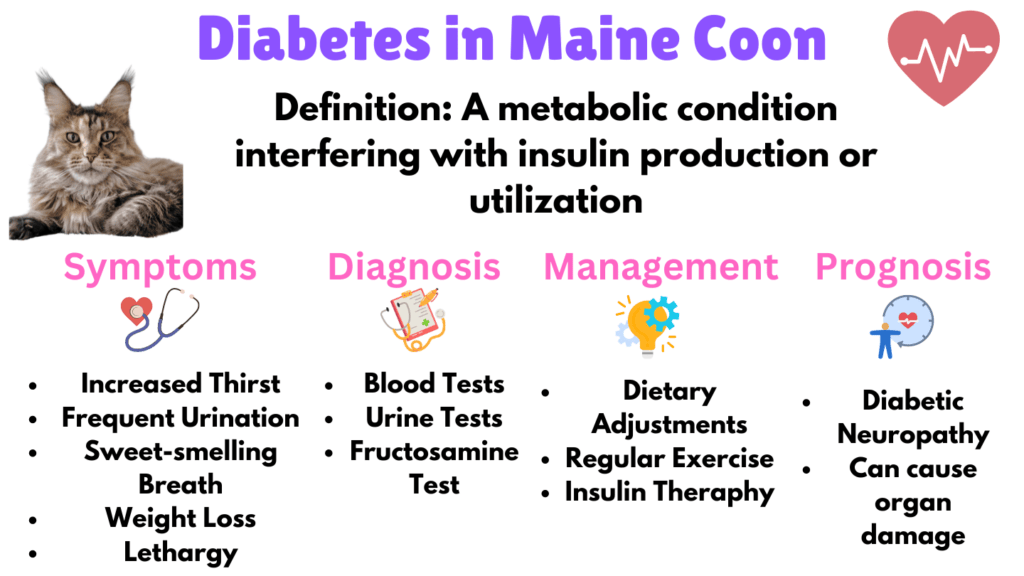
Diabetes Mellitus is a metabolic condition that disrupts insulin production or use, affecting blood sugar levels. Symptoms include increased thirst, frequent urination, increased appetite, weight loss, and lethargy. If not managed properly, diabetes can lead to organ damage, diabetic neuropathy, and an increased risk of infections.
8. Dental Problems
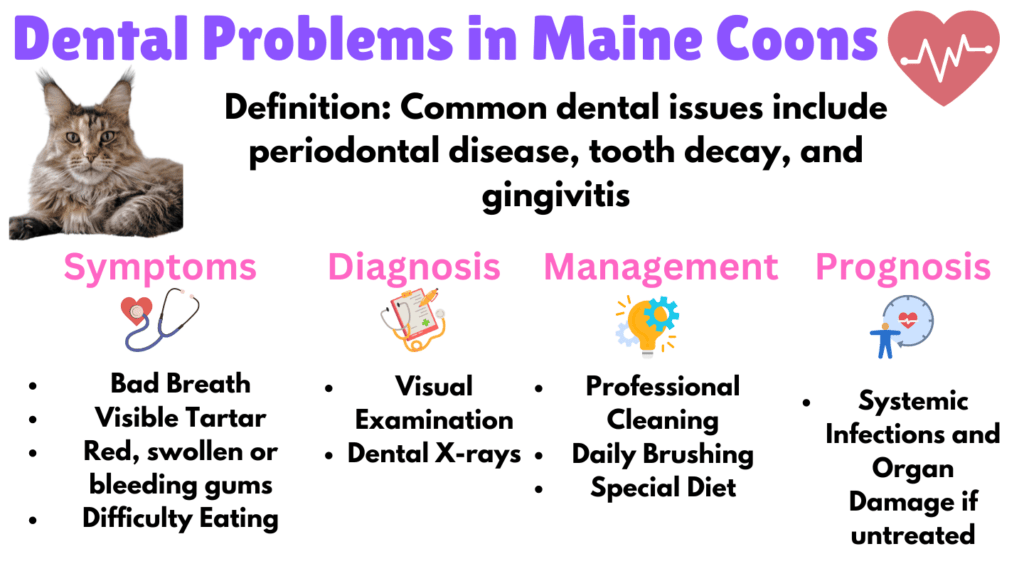
Dental problems such as periodontal disease, tooth decay, and gingivitis are common in Maine Coons. Symptoms include bad breath, tartar buildup, red or swollen gums, and difficulty eating. Untreated dental issues can lead to bacteria entering the bloodstream, poor general health, and weight loss.
9. Heart Disease
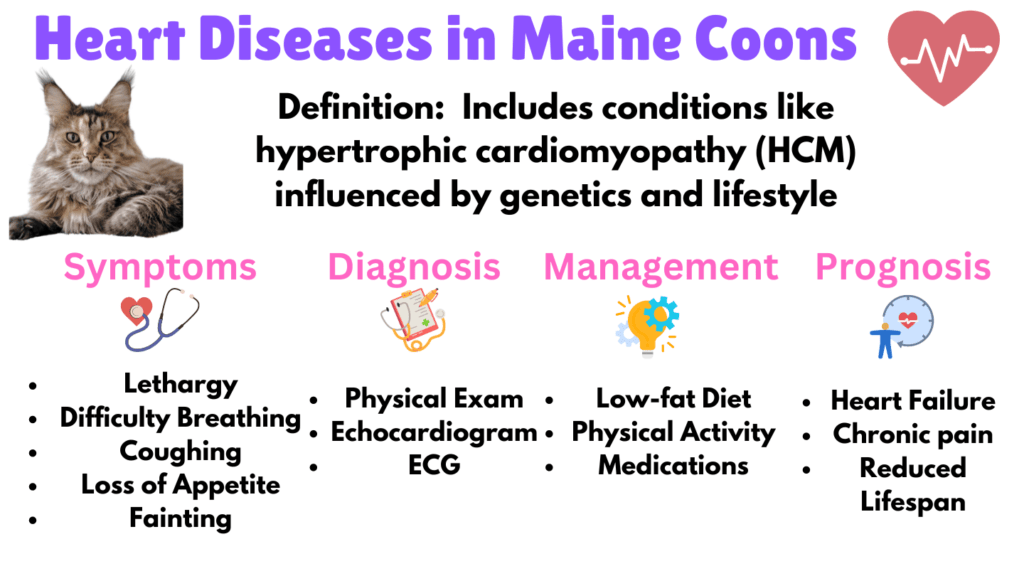
Apart from Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM), Maine Coons can suffer from other heart problems influenced by genetic and lifestyle factors. Symptoms include lethargy, difficulty breathing, coughing, loss of appetite, and fainting. Heart disease impacts the cat by potentially leading to congestive heart failure, thromboembolism, and chronic pain.
10. Stress and Anxiety
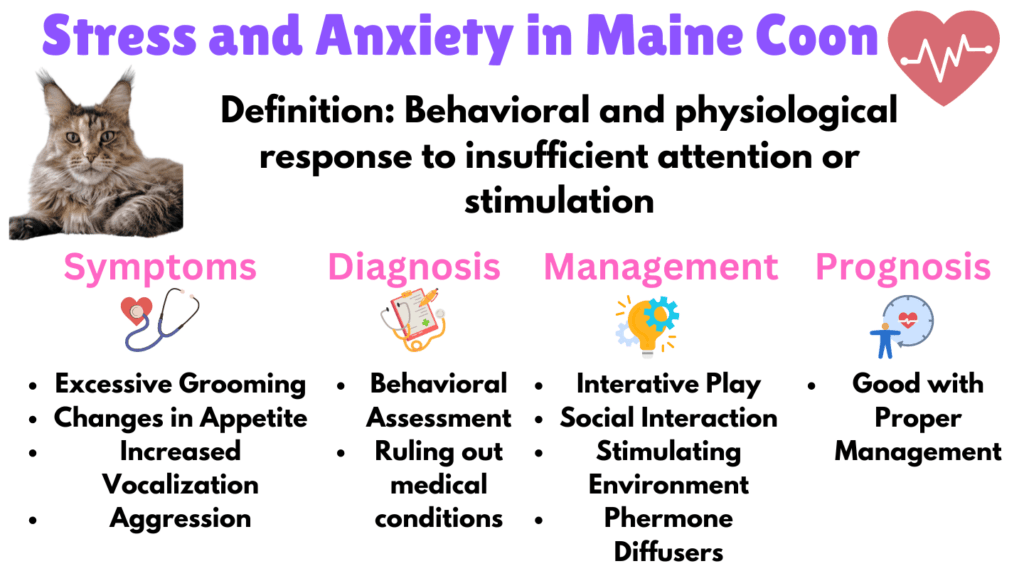
Maine Coons are social and can suffer from stress and anxiety if they lack attention or stimulation. Symptoms include excessive grooming, changes in appetite, increased vocalization, hiding, and aggression. Chronic stress can weaken the immune system, lead to behavioral issues, and strain the pet-owner bond.
11. Gastrointestinal Issues
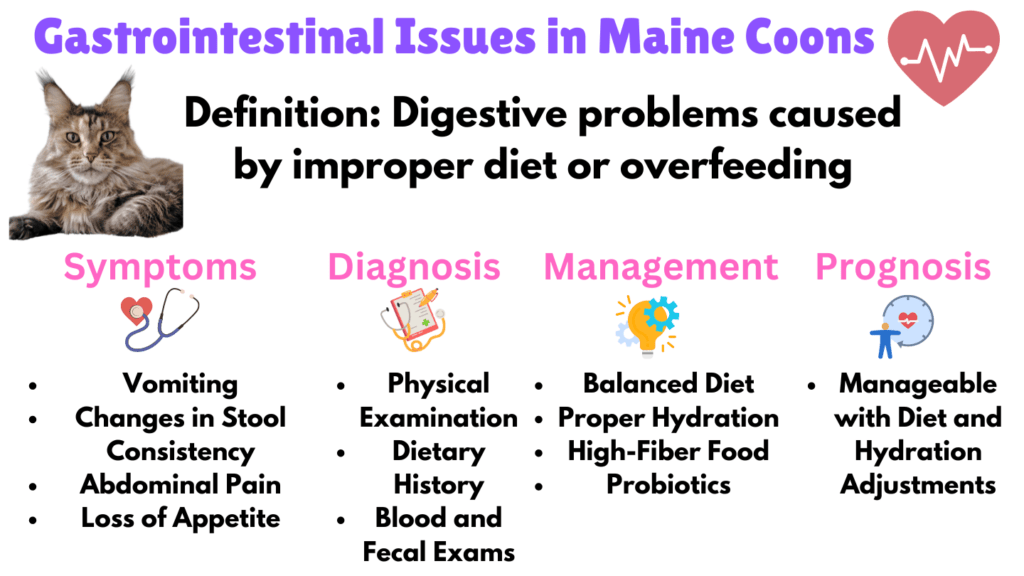
Gastrointestinal issues in Maine Coons can result from overfeeding or an improper diet, leading to constipation or diarrhea. Symptoms include vomiting, changes in stool consistency, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, and lethargy. Chronic digestive issues can cause dehydration, malnutrition, and reduced activity.
12. Skin Problems
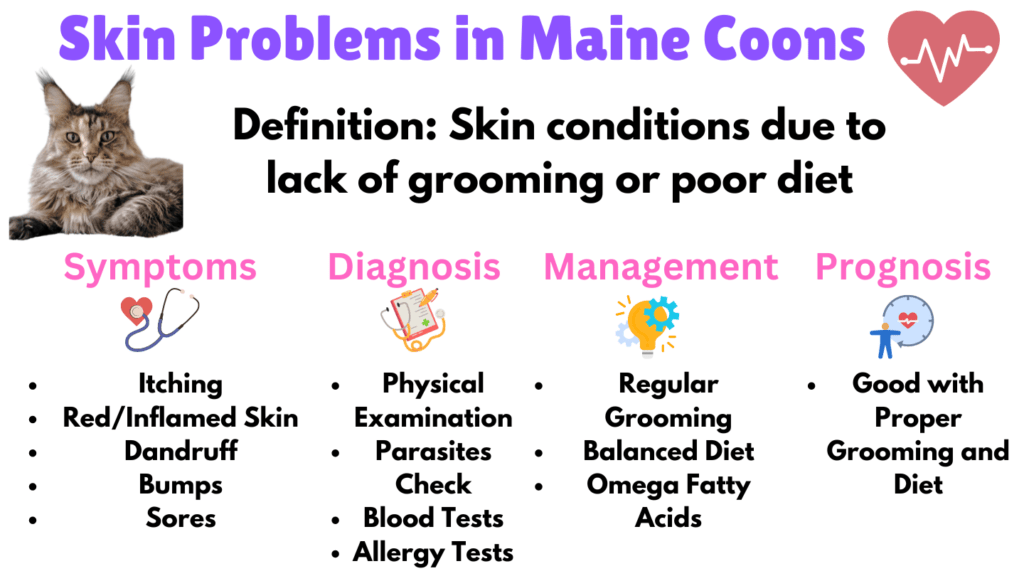
Maine Coon cats are known for their luxurious coats, but maintaining their skin and fur health requires diligent care. Symptoms of skin problems include itching, red or inflamed skin, dandruff, bumps or sores, and changes in coat quality. Chronic skin irritation can lead to secondary infections, chronic irritation, and hair loss.
Preventive Care for Maine Coon Cat Health
Ensuring your Maine Coon cat lives a long, healthy life involves proactive care and early detection. Here are key strategies:
- Regular Vet Visits: Schedule annual check-ups, vaccinations, and routine health screenings to catch issues early.
- Healthy Diet and Hydration: Provide a balanced diet tailored to Maine Coons and encourage hydration with fresh water sources or water fountains.
- Regular Exercise: Engage your cat with interactive toys, puzzle feeders, and activities to keep them active and stimulated.
- Managing Chronic Conditions: Use medications and lifestyle adjustments for long-term health issues. Genetic testing can help detect and prevent serious problems early.
- Mental Well-being: Reduce stress by creating a cat-friendly environment with cozy spaces and interactive play. Mental stimulation helps prevent stress-related behaviors and promotes overall happiness.
Common Myths on Maine Coon Cat Health Issues
Myth 1: Maine Coons have poor health
Fact: This is totally bogus! The health of a Maine Coon hinges on factors like housing conditions, diet, stress levels, and veterinary care—not just the breed itself. Maine Coons typically have a lifespan of 12-15 years, with many living up to 20 years or more if well taken care of. Responsible breeders meticulously screen for genetic diseases to ensure healthy, purrfectly content kittens.
Myth 2: Maine Coons weigh 20-30 kg (44-66 Lbs)
Fact: That’s a colossal exaggeration! Male Maine Coons typically tip the scales at 6-8 kg (13-17 lbs) , with the biggest boys reaching 11.5 kg (25 lbs). Females are more petite, usually weighing in at 4.5-6.8 kg (10-15 lbs). Their large size often leads to wild overestimations of their weight.
Myth 3: Maine Coons need a lot of space and can’t live in apartments
Fact: Nope, Maine Coons can totally rock apartment life! With some smart organization of vertical space, these majestic furballs will happily perch and climb their way through a compact living space. They just need spots to survey their kingdom from above.
Myth 4: Maine Coons eat a lot
Fact: While they might chow down more as rapidly growing kittens, adult Maine Coons don’t have an excessive appetite compared to other breeds. The focus should be on high-quality, nutrient-dense food rather than sheer quantity.
Myth 5: Maine Coons are naturally resistant to health problems due to their size
Fact: Size doesn’t make them immune to health issues. Like any other breed, Maine Coons can face genetic and lifestyle-related health problems. Regular vet check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are key to keeping them in tip-top shape.
Myth 6: Maine Coons don’t need much exercise
Fact: Regular exercise is a must to keep these big beauties from turning into couch potatoes. Maine Coons thrive on interactive play and physical activity, which help prevent obesity and related health issues.
Maintaining the Well-Being of Your Maine Coon
Caring for Maine Coon cat health issues is a responsibility that not only improves their quality of life but also enhances ours. By focusing on preventive care and early detection, we can manage lifestyle-related health problems and ensure our cats stay active and happy.
Remember, the bond we share with our pets is mutually beneficial, enriching our lives every day. This comprehensive post about all the health issues of Maine Coon cats serves as your guide to providing the best possible care for your gentle giant.
Meet Sean, a fintech whiz with a penchant for pet purrs and blockchain buzz. After a decade of fintech feats, Sean's tech talents leaped from ledger lines to litter lines, driven by a passion for pets and a vision for a more connected pet care community. With three critter companions as co-pilots, Sean launched this blog to share a treasury of pet-friendly tech tips and tales.